Intestinal permeability sets fire to your immune system
Before you "eye roll" the term "Leaky Gut" consider what is happening
The term leaky gut is sort of an Instagram Friendly way of describing Intestinal Permeability….a term used to describe when the gut is overly permeably.
In the Intestinal Permeability scenario microbiome, antigens, and large protein debris (Endotoxins) from the gut gets translocated into the immune layers of the intestinal wall .
Metabolic Endotoxemia is a term that describes when endotoxins(like Lipopolysaccharide) from the gut move through the intestinal wall into the blood, lymphatics, and organs (ie. liver, brain, skin, etc.)
Much of the research is that has been done in this comes from the world of acute sepsis , however, much research is developing in understanding the immune effects of chronic intestinal permeability
The consequences of chronic endotoxemia are immune activation. In fact some of the identified immune factors are:
Interleukin-1-beta secretion: : IL-1β is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is frequently released in response to endotoxemia. It plays a major role in systemic inflammation and fever.
Myocardial Depressant Factor Secretion: endotoxemia can result in the release of myocardial depressant factors (MDFs), which impair heart function. These factors are often associated with cytokines like IL-1β and TNF-α.
Anaphylatoxins C5a and C3a Secretion: C3a and C5a are produced during the activation of the complement system, which occurs during endotoxemia. They promote inflammation and recruit immune cells.
Platelet Activating Factor: (PAF) is indeed secreted during endotoxemia and plays a role in inflammation, platelet aggregation, and vascular permeability.
Oxygen-Derived Free Radicals: Endotoxemia stimulates the production of oxygen-derived free radicals (reactive oxygen species, ROS) by immune cells like macrophages and neutrophils, leading to oxidative stress and tissue damage.
Bradykinin Secretion: Bradykinin is involved in increasing vascular permeability and promoting inflammation, and its levels may rise during endotoxemia.
Beta-Endorphins: Beta-endorphins, which modulate pain and immune responses, are released as part of the body’s stress response to endotoxemia and inflammation.
Prostaglandin, Thromboxane, Leukotriene, and Prostacyclin Release: These eicosanoids are inflammatory mediators released in response to endotoxemia, promoting inflammation, platelet aggregation, and vasodilation.
Activation of the Coagulation System: Endotoxemia activates the coagulation system
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF): TNF-α is a key cytokine released during endotoxemia. It plays a central role in initiating the inflammatory cascade and can contribute to septic shock if dysregulated.
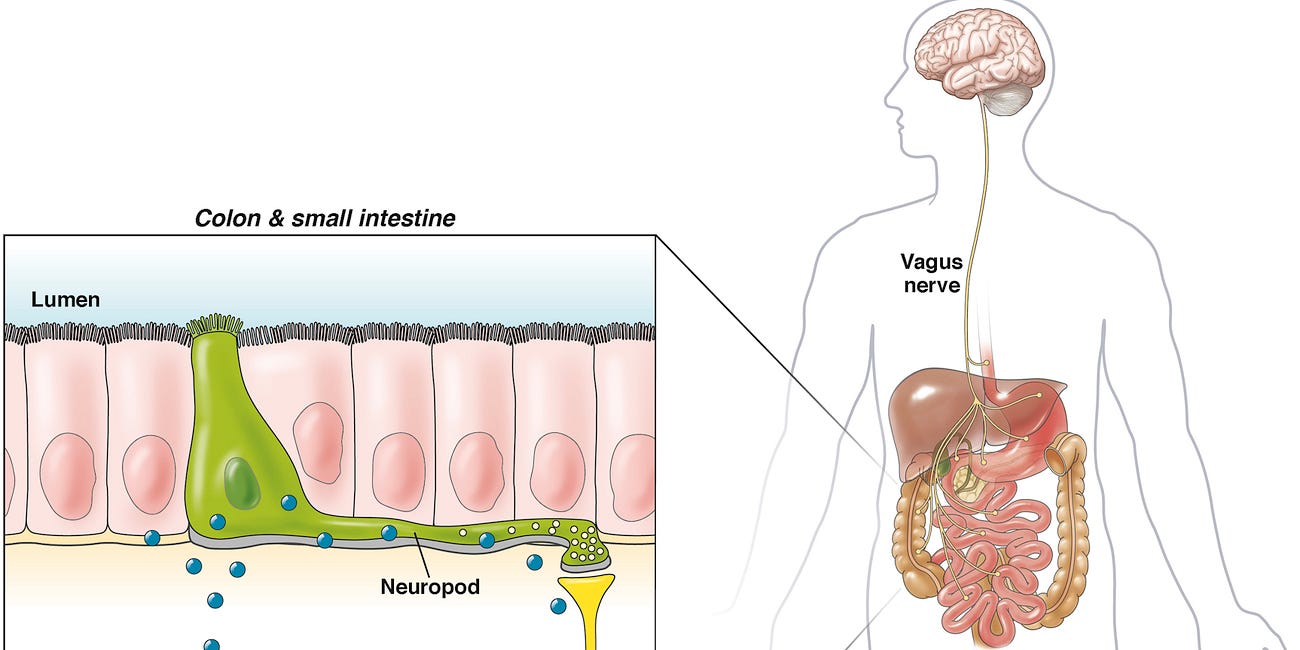
I am always writing about the gut/brain axis, the gut/liver axis, the gut/skin axis and many other interrelations. Now we know the common denominator.
Now it is important to understand that it is not always the chicken (gut issues) and egg ( intestinal permeability). Sometimes there are other drivers that are keeping the gut extra permeable. For example intestinal permeability maybe be caused by other toxins (metal toxicity), medications, chronic stress disorders, medications, autoinflammatory conditions (ie. psoriasis), and autoimmune conditions (like IBD/RA )
So yes, we must keep the “eye roll” going strong for most of the things we see on IG but this barrier thing is legit and we need to keep leaning in and learning about it.
Related posts:
How does the Brain-Gut-Axis really work?
"Does it make sense in your brain, feel right in your heart and gut?"