When we think of neurologic disorders like Dementia , Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Diseased, Multiple Sclerosis, and Autism we are left with a lot of why questions and a lot of theories. Most neurologic disorders involve issues with neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and mitochondrial problems. And finding the root cause is subject to tremendous research and therapeutic trials. I was introduced not too long ago to plasmalogens as a biomarker.
And to be honest I had only heard the term once by a famous lipidologist Dr. Mark Houston when he spoke on cardiovascular disease. So as a newbie I wanted to find out why plasmalogens are seen to be a link and possible way to prevent and support these troubling conditions. So recently interviewed Dr. Dayan Goodenowe of Prodrome Sciences for my podcast and dove into this topic (scroll down). I really feel this information needs to be shared. Below is some overview.
What is a plasmalogen?
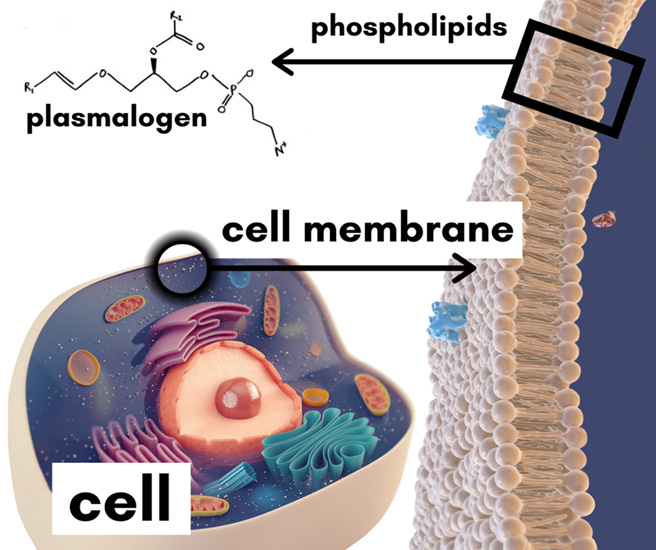
A plasmalogen is a phospholipid in the body with a ether bond in the sn-1 position to an alkenyl group. This is heavy science for sure but the picture below might help.
Phospholipids the are major constituents of the membranes of cells and intracellular organelles and vesicles. They give shape, fluidity, structure, and a communication medium to our organs, organelles, cell membranes, and vesicles.
Plasmalogens are largely thought to be to function as an antioxidant against reactive oxygen species. They also are thought to be involved with cell signaling. There has been associative data to suggest that low levels of plasmalogens are associated with Parkinson's Disease, Dementia, Alzheimer's Disease, and Multiple sclerosis. And even stronger evidence the the levels being lower are associated with cognitive decline. (see Su XQ, Wang J, Sinclair AJ. Plasmalogens and Alzheimer's disease: a review. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):100. Published 2019 Apr 16. doi:10.1186/s12944-019-1044-1)
They seem to be important in keeping our nervous tissue from being inflamed, degenerating, and dysfunctional. As far as memory is concerned they have a particular deep role in helping with acetylcholine transmission which is the link to cognition.
Plasmalogens are found in numerous human tissues, with particular enrichment in the nervous, immune, and cardiovascular system. Cells are made up of phospholipids. (that is what keeps cells fluid and able to maintain form and communication). Plasmalogens are found in the phospholipids and synaptic clefts of many tissues. In human heart tissue, nearly 30–40% of choline glycerophospholipids are plasmalogens. In the human heart 32% of the glycerophospholipids are plasmalogens. 20% of the brain is made up of plasmalogen. And 70% of the myelin sheath ethanolamine glycerophospholipids are plasmalogens.
Plasmalogens are made in peroxisomes in the liver. This part of the liver is responsible of using lipids/fats for various body needs. In fact this is where cholesterol and bile is made. Peroxisomes use lipids to synthesize plasmalogens. As we get older our liver function slows down and the production of plasmalogens declines. Hence we may be more susceptible to oxidative stress in the brain, liver, and immune system.
Sadly you cannot eat plasmalogens. If there are plasmalogens in your food (ie. a beef steak) they will not survive stomach acid. However, you can make plasmalogens with exercise.
There are blood tests available now that offer plasmalogen profiles. These can be done through Prodrome Sciences. These tests comprehensively scan for deficiencies in plasmalogens . They look for markers in :
Membrane Lipids
Ethanolamine Plasmalogens
Choline Plasmalogens
Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
Phosphatidyl choline
Sphingomyelins
Cholesterol
Membrane Lipid breakdown products
Lysophosphatidyl choline
Phosphorylcholine
Diacylglycerols
Ceramides
Free fatty acids (DHA, DPA, EPA, AA, LA, OA)
Lipid storage
Triacylglycerols
Anti-inflammatory lipids
Gastrointestinal Tract Acids GTAs
Key Lipid ratios
Omega-3/6
Omega-3/9
Plasmalogen choline to Phosphatidylcholine
Ethanolamine plasmalogen to Phosphatidyl ethanolamine
Sphingomyelin to Ceramide
With this information you can replete plasmalogens with newly available plasmalogen precursor supplements. These supplements survive the stomach acid as a precursor and reportedly will transform into active plasmalogens once they are absorbed and sent to the liver.
On the surface the supplement appears to be similar to DHA fish oil however it is different. According to formulator and inventor Dr. Goodenowe; in regular omega-3 supplements the DHA/EPA/DPA are attached to a tri-acyl glycerol backbone. This is the regular oil backbone. However in plasmalogen precursors such as (prodromeneuro); DHA/DPA/EPA is attached to an Alkyl-acyl glycerol backbone. This is what makes it a plasmalogen precursor. That form allows the liver to synthesize this into a plasmalogen. Again referring back to the diagram on plasmalogen synthesis we see that we are absorbing a precursor to plasmalogens.
I am very encouraged that plasmalogens provide a piece of the puzzle that was missing. I am offering testing of plasmalogens and appropriate repletion strategies. I am even trying them out to help with my brain health. Find out more information by reaching out at www.soundintegrative.com Below is a continuation of this topic with podcasts below
Link to Podcast:
Links mentioned in the episode